Liquid Gravity
SIMS
Stability Island
Mapping
Survey
Looking for the legendary Stability Island through Binding Data
Looking for the legendary Stability Island through Binding Data

What would you do, if you just found a way to explore the fabled island of stability? You would tell the world and hopefully you would find some hearty soles to join you on your quest!
Like so many intrepid explorations, there is a quest to discover something new and beat the others, who are attempting to make the journey into the unknown. There is a myth among scientists that there is an island beyond the shores of our periodic table that contains unfathomable treasures with new and amazing powers. Sounds like a fairytale but there has been a real ongoing competition between countries to be the first to discover this island. USA, Russia and now Germany have all made progress towards finding it, with recent claims they are at the shoreline of this fabled island. https://www.sciencenews.org/article/sailing-toward-island-stability
So far Scientist have employed massive particle accelerators and blasted particles at atoms in an attempt to see if they can form new isotopes. Sometimes they have been lucky enough to make something stick long enough to measure it and claim the prize of naming their discovery. Moscovium, Germanium, Californium, just to name a few. They have discovered five new elements (113, 114, 115, 116, and 118) over six years. It's a serious and expensive business..
Now there is a new way to explore the uncharted oceans beyond our periodic table, that you can be part of. We are building new software that maps all of the existing atoms, and uses existing data to program new algorithms for predicting new isotopes.
You would think that has been done already and the existing atomic models would be enough for scientists to use. Their existing models are over 80 years old and their predictions of magic numbers and shell structures have failed in recent research projects.
One such project that took over 8 years of research was oxygen 28 that was meant to have double magic properties and be very stable, however it wasn't at all magic and fell apart in subsecond speed. Another project was the discovery of the lithium halo nucleus that had orbiting neutrons, which wasn't anything like what had been predicted!
Technetium-97 has a long half life of 4.2million years but when your compare it with its neighbor, Technetium-96, it has a very short half life of only 4.28 days! The big question that scientists are trying to figure out is why does only one neutron make such a big difference?
By using the new SIMS method to map the structure of Technetium-96 we find an orphan neutron that hadn't been properly coupled and this triggers their decay process.

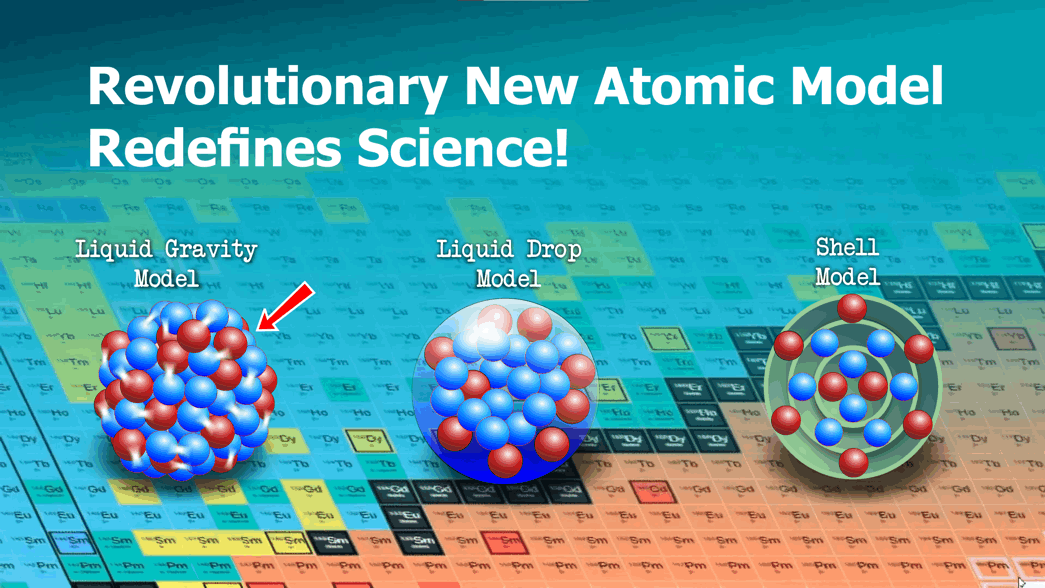
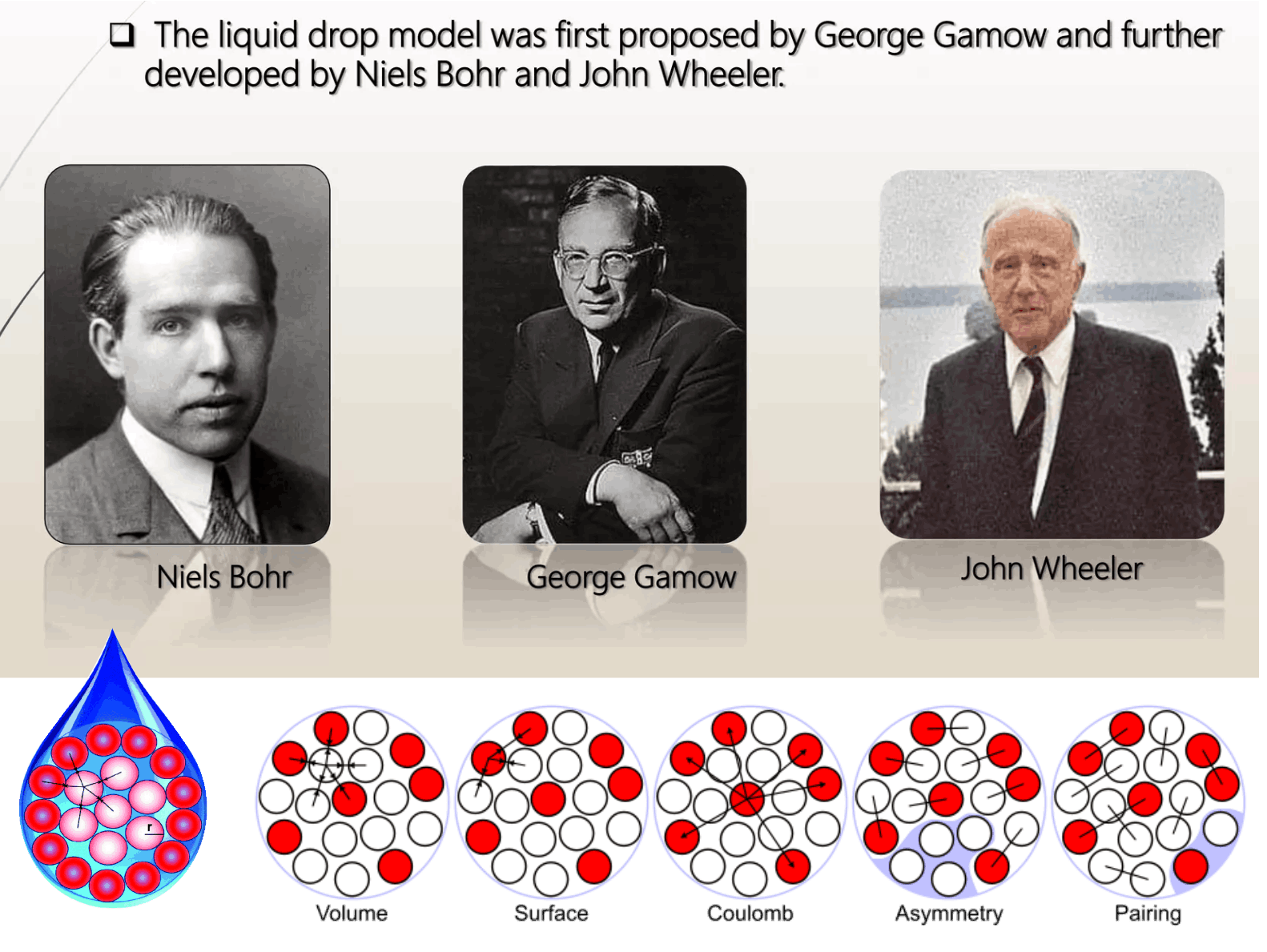
Scientist use a method called the Liquid Drop model to estimate the properties of atoms. Binding Data is a property of atoms that is able to be measured by weighing an atom and deducting the mass of its components. The result is less than the sum of its parts, which somehow lose weight (mass) by being a whole atom. This missing mass is called binding data. Unfortunately for the scientist, they haven't worked out how this process works and their best method of calculating binding data has a high error rate. Their Liquid Drop Model, is around 1-2% error rate for heavy atoms and 25-300% error rate for some lighter elements. Their method uses 5 different factors which start off as a broad volumetric calculation and then is refined based on a number of assumptions. The problem with this method is that it is an unreliable tool for mapping the properties of new or extreme atoms. It cant predict or map the uncharted areas beyond the periodic table.
The SIMS model is a new method of calculating the binding mass of each atom with a lower error rate of 0.2%. SIMS uses 6 assumptions to calculate binding energies in a nucleus. It assumes that nucleuses are assembled using very exact formations that follow strict rules. Using this method, allows us to find out more about the atom, such as calculating specific binding energies for each individual nucleon, rather than just the average binding energies. It also can identify the likely beta decay triggers such as too much positive or negative balance, structure stacking weakness, and explosive orphans. The strict set of rules also tell us about how nucleons work and the functions of their internal subatomic particles.
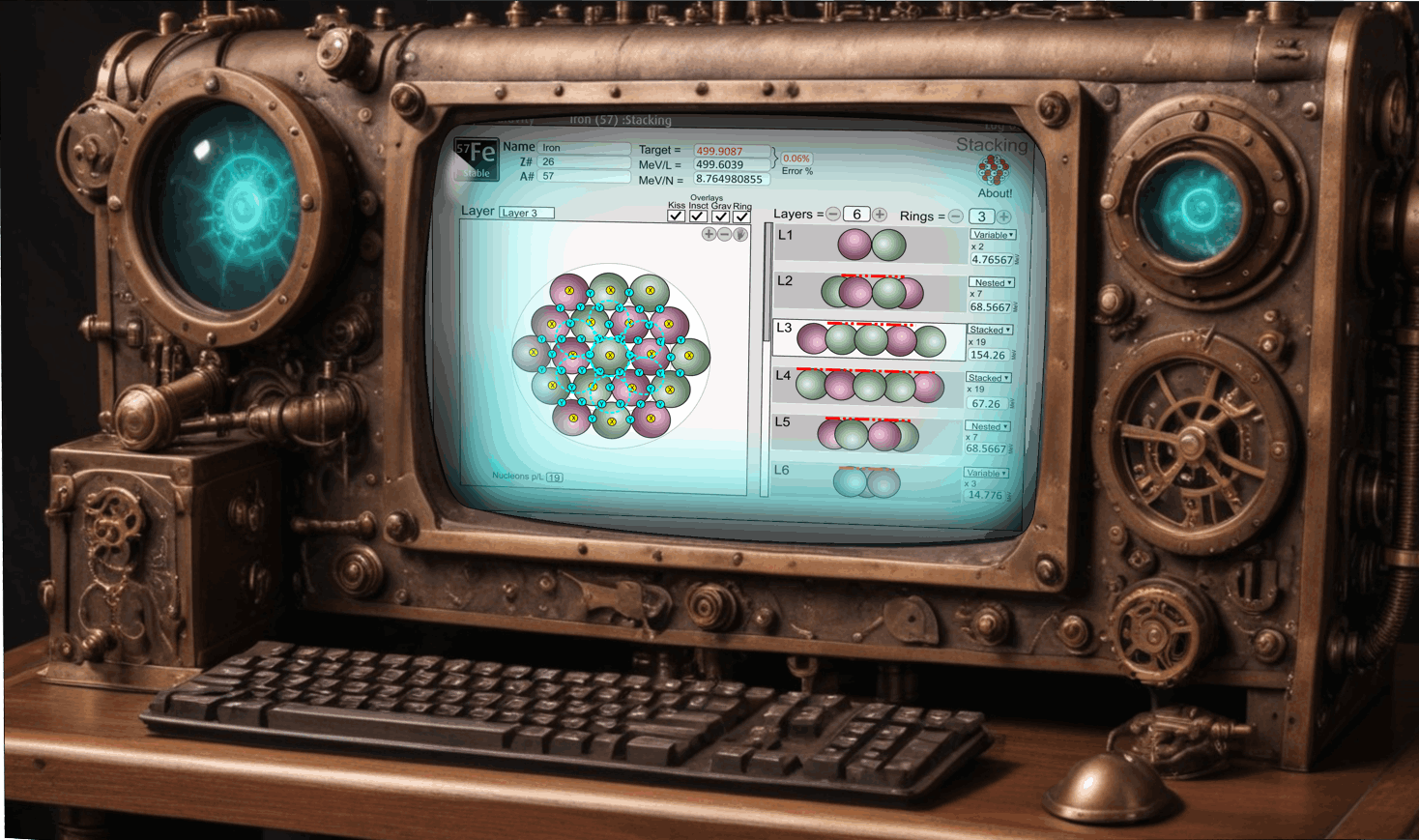
The SIMS method takes a very different approach to calculating the Binding Energy of atoms. It uses 6 different factors to not only work out the the missing mass, but also to identify where atoms show signs of beta decay and what causes it. The SIMS method also uses a different theoretical model that suggests that strong and weak nuclear force are simply are emergent forces of gravity. This is an important distinction based on a different understanding of gravity and how it works. There are 6 key factors that need to be considered when calculating the properties of an atom.
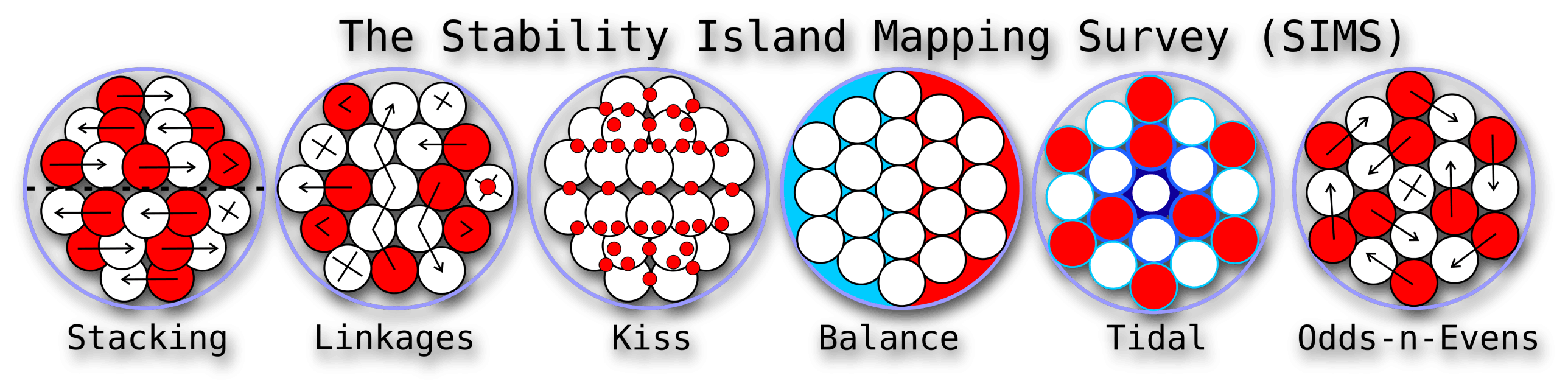
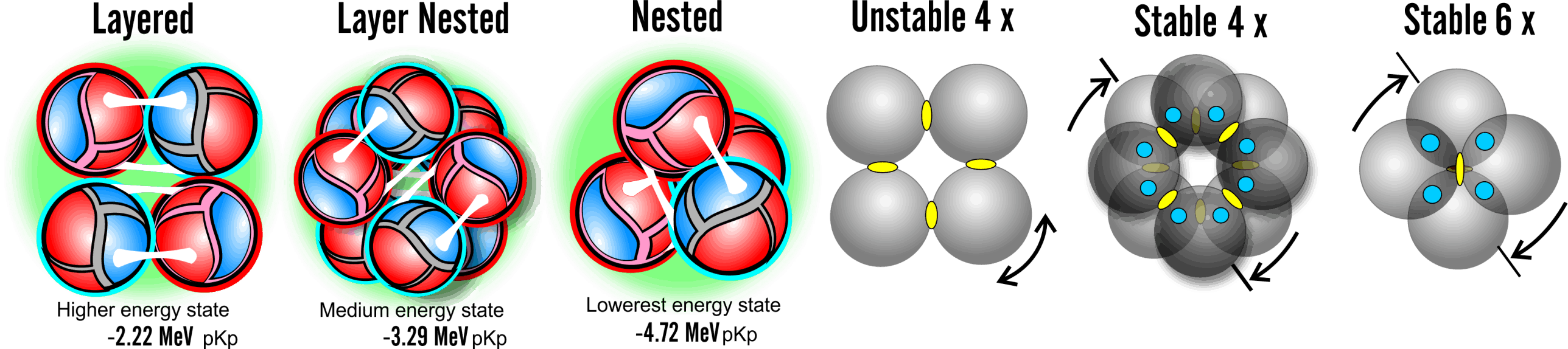
The Liquid Drop Model suggests that atoms are like a bag with atoms stacked in a random order and may even be sloshing around. The SIMS model suggest that atoms are very precisely stacked with exact order that remain constant within each isotope. The key observation with stacking nucleons together is that they go through stages, from stable to unstable, then they collapse into a new configuration, as their nucleon count increases. Atoms are constantly vibrating and this causes them to cluster together in their tightest and most optimal way. As nucleons increase, the structure changes and these changes can have a direct bearing on their fission stability.
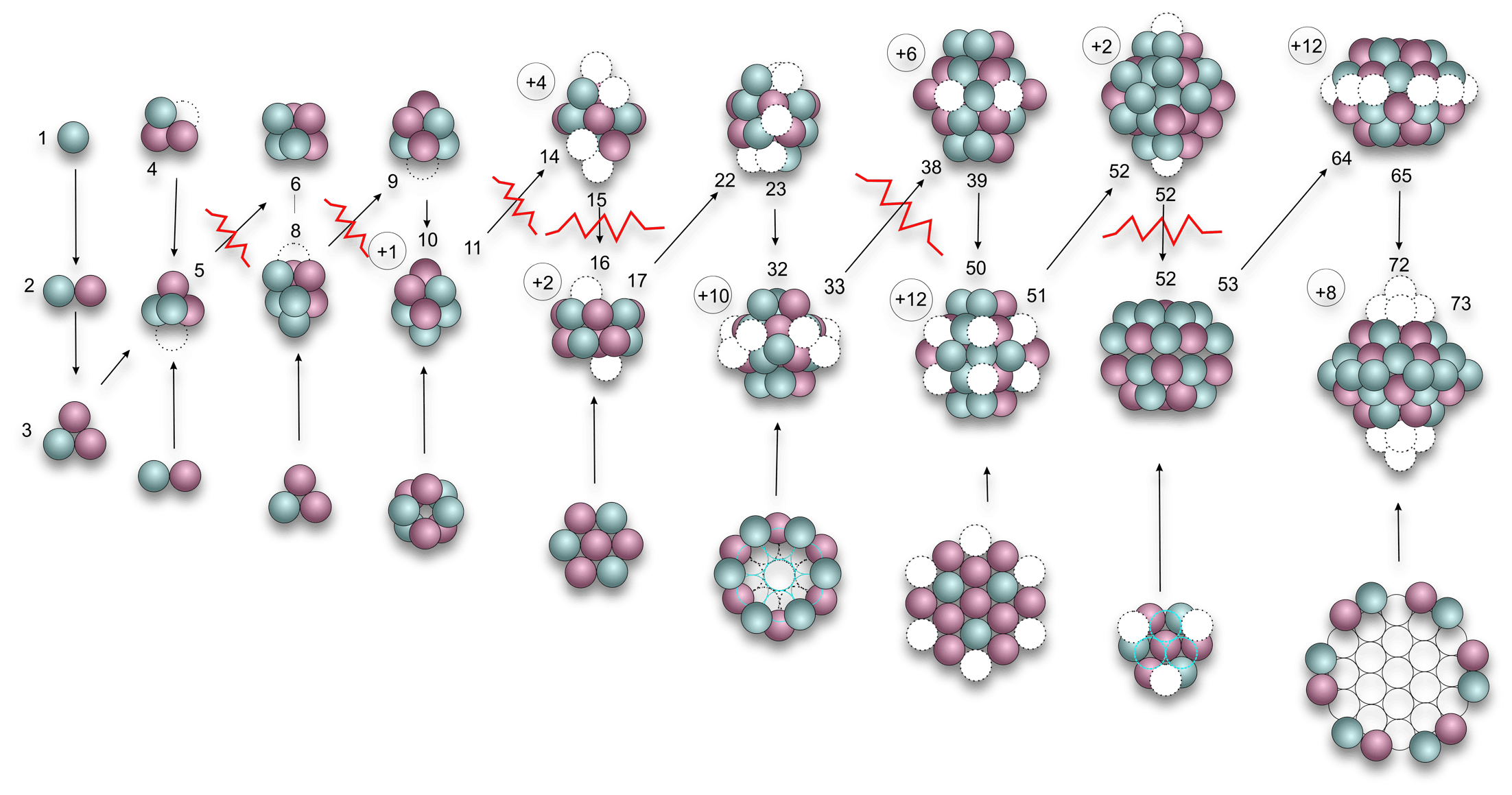
Atoms are not made up of independent nucleons. Protons link to Neutrons and form into pairs or chains. Some of these linkages are very stable and others can cause delayed collapse of the atom. by understanding the rules that govern good and bad linkages we can better understand the reason why some isotopes are stable and others suffer from beta decay. We need to understand the mechanism of protons and neutrons and how their linkages facilitate the distribution of energy. We also identify what makes a proton attract a neutron, and not another proton. Also why a proton can survive on its own and a Neutron cant.
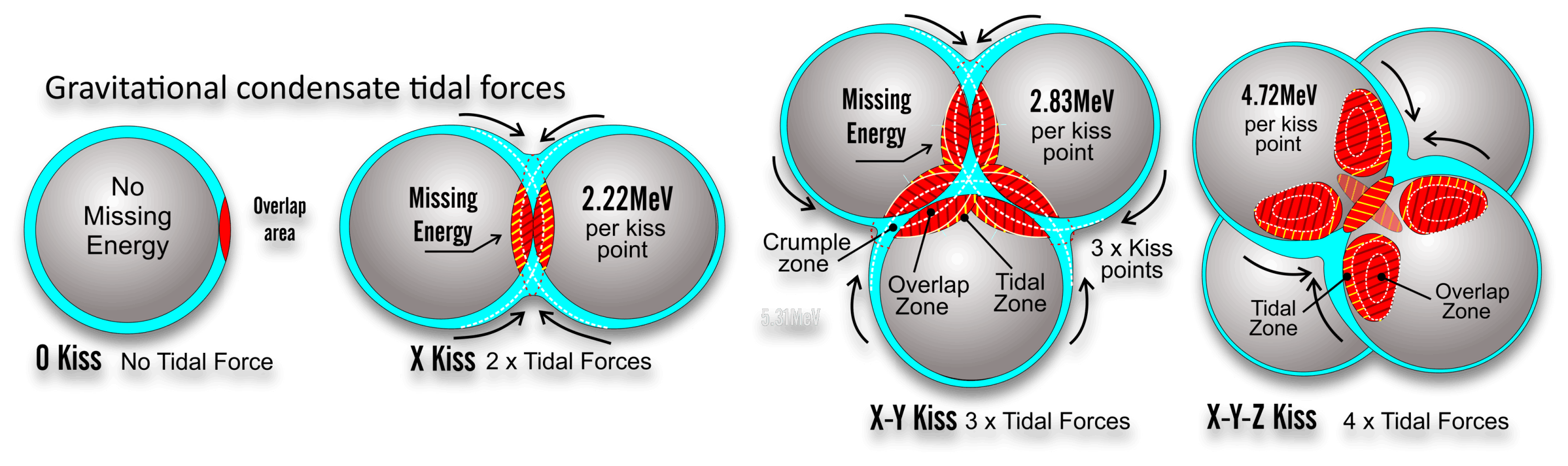
Kiss points are the locations that each nucleon touches each other. Hydrogen1 has no kiss points and heavy atoms have hundreds of kiss points. Each kiss point has a different binding energy value and these variations range based on how the nucleons are stacked together. Within each atom there are different areas that are close to each other or at right angles to each other. In order to calculate the accurate binding energy of an atom each kiss point needs to be identified and sorted based on its proximity to other kiss points. As a rule, closer kiss points produce higher binding energy levels.
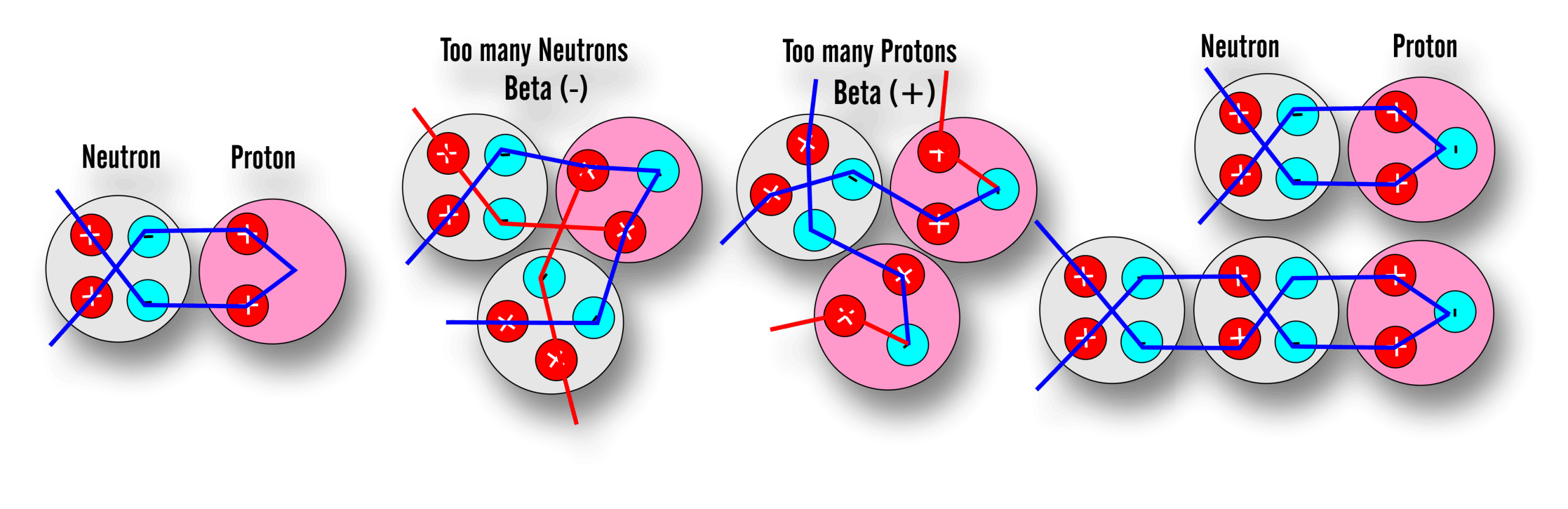
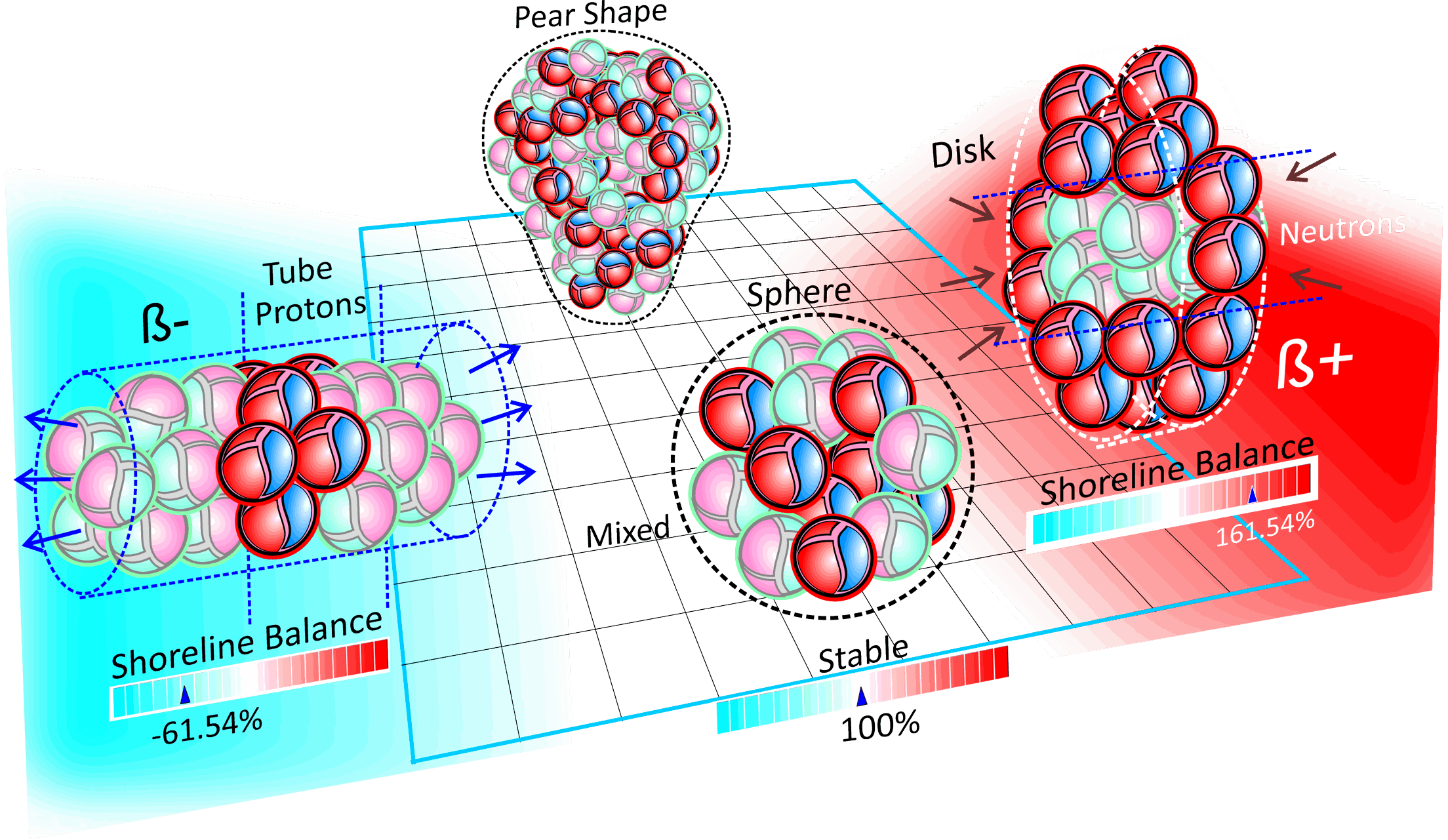
Balance is the main feature that is evident when you study the stability tables showing a valley of stability running between Beta (+) on one side and Beta(-) on the other side. This balance is a combination of positive and negative pressures that build up within each atom. The Bets(-) is the build up of gravitational condensate from within each nucleon, and the Beta(+) is the result of too much external positive pressure emitted from nucleons. Each atom's stability is dependent on staying within a range of positive and negative pressure balance. The key to calculating this balance zone is by comparing it to a tidally affected shore line. In the case of atoms, nucleons get covered up with increasing numbers of kiss points and increasing gravity. This reduction in shoreline produces less gravitational radiation (Beta-) per nucleon, which requires more nucleons to offset the (Beta+) positive field.
Tidal effects are always associated with gravity. In this case we see each nucleon covered in a layer of gravitational condensate that is slowly excreted out from both neutrons and protons. This condensate is liquid and gravitationally attracts towards the center of each cluster. The condensate is displaced around the kiss points but builds up in a tidal fashion. This increase in depth displaces more condensate which accounts for the increase in the loss of more mass.
A right angle kiss point has a low loss of mass but nested kiss points have a very high loss of mass due to the increased gravitational pressure over smaller distances.
Within each isotope there is a subtle difference in binding data based on whether it has an odd or even number of nucleons. This subtle difference comes down the nucleon linkages forming a closed or open loop. All the pairs and chain connections ultimately form into a single magnetic circuit which results in an outward or inward pressure on the last link in the chain. Outward pressure will open up the last kiss point and decrease the binding energy , and the inward pressure would close the last kiss point to make an increased binding energy.
We are looking for interested people to join our expedition by supporting us though Kick starter or by being part of our software development process. This is an independent project that is not supported through research institutions because it uses a different theory of how atoms work. The aim of this project is to build a complete catalogue of existing atoms and use the data to form a method to survey uncharted atoms beyond the periodic table.